Folic Acid Impurities: Reference Standards for Pharmaceutical Quality Control
Folic Acid, also known as Vitamin B9, is a water-soluble B vitamin essential for numerous biological processes—from skin renewal and red blood cell production to fetal neural tube development. Like most vitamins, a balanced diet generally meets the daily requirement of folic acid for healthy individuals.
Insufficient folic acid in the body can lead to impaired DNA synthesis in red blood cells, preventing their proper maturation and resulting in megaloblastic anemia. For women who are planning pregnancy or are in the early stages of pregnancy, adequate folic acid intake significantly reduces the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus. Therefore, selecting high-purity, high-quality folic acid supplements is crucial.
To ensure the safety and efficacy of folic acid supplements, strict limits for related impurities have been established. The Chinese Pharmacopoeia(2025 Edition) specifies that in the chromatogram of the test solution, the peak area of pteroic acid or any other individual impurity must not exceed 0.6 times the peak area of the reference solution‘s main peak (0.6%). The sum of all impurity peak areas, excluding the pteroic acid peak, must not exceed 2 times the peak area of the reference solution‘s main peak (2.0%). Peaks with an area less than 0.05 times that of the main peak in the reference solution should be disregarded. Additionally, the International Pharmacopoeia and relevant drug regulatory agencies have imposed stringent controls on impurity levels.
Beyond process-related impurities, factors such as light exposure, high temperatures, or humid conditions can cause the oxidation or degradation of folic acid, leading to the formation of new impurities. Different impurities can variably impact the drug‘s efficacy, making it necessary to control their respective levels to ensure the purity and safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and mitigate potential health risks.
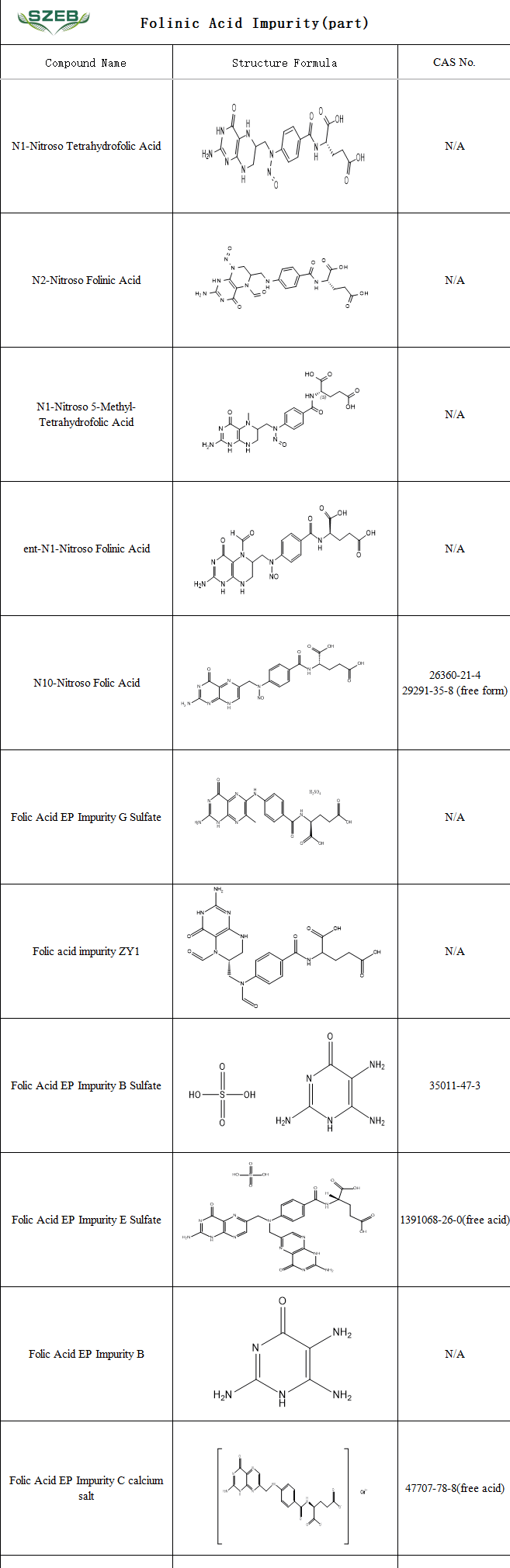
SZEB supplies a range of folic acid impurity reference standards, including folic acid nitrosamine impurities, USP/EP listed impurities, chiral/stereoisomer impurities, and other structural analogs. These products support pharmaceutical companies in the accurate identification, analysis, and evaluation of potential impurities, thereby ensuring drug safety and efficacy while accelerating the review process for generic drug development.
Below is a partial list of available impurities. For more details, visit our official website: www.ex-biotech.com
Email: sales@ex-biotech.com.






.jpg) Wechat
Wechat