CCBs Nitrosamine Impurities——Precise Drug References Empowering Drug Safety Across the Entire Lifecycle
Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, commonly referred to as CCBs, are cornerstone medications in hypertension management. Key examples include amlodipine, nifedipine, nimodipine, nitrendipine, felodipine, and lercanidipine. Their mechanism of action involves inhibiting calcium ion influx into smooth muscle cells of the heart and vasculature. By inhibiting calcium-dependent contraction, CCBs promote vascular relaxation and dilation, reduce peripheral resistance, and decrease cardiac workload, thereby effectively lowering blood pressure .
Nitrosamine Impurity Risk and Regulatory Evolution
The dihydropyridine ring in their chemical structure is theoreticallysusceptible to nitrosamine formation, placing CCBs on the list of pharmaceuticals requiring nitrosamine impurity risk assessment. Since the 2018 detection of N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) in valsartan products, global regulatory agencies have mandated comprehensive risk evaluations for all chemically synthesized active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Consequently, oversight of nitrosamine impurities has intensified significantly .
June 2020: EMA published the Assessment Report for Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Medicinal Products.
September 2020: FDA issued the guidance Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in HumanDrugs, identifying three primary sources (process-related, cross-contamination, degradation) and requiring lifecycle control strategies.
August 2023: FDA released Recommended Acceptable Intake Limits for Nitrosamine Drug Substance-Related Impurities (NDSRIs), classifying NDSRIs into five categories based on carcinogenic potency and setting Acceptable Intake (AI) limits (26.5–1500 ng/day). Notably, N-Nitrosoamlodipine, N-Nitrosnifedipine, and N-Nitrosnicardipine were classified as Category 5 (low risk) with an AI of 1500 ng/day.
September 4, 2024: FDA updated its guidance with the second edition of Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs.
Current Regulatory Focus and Industry Response
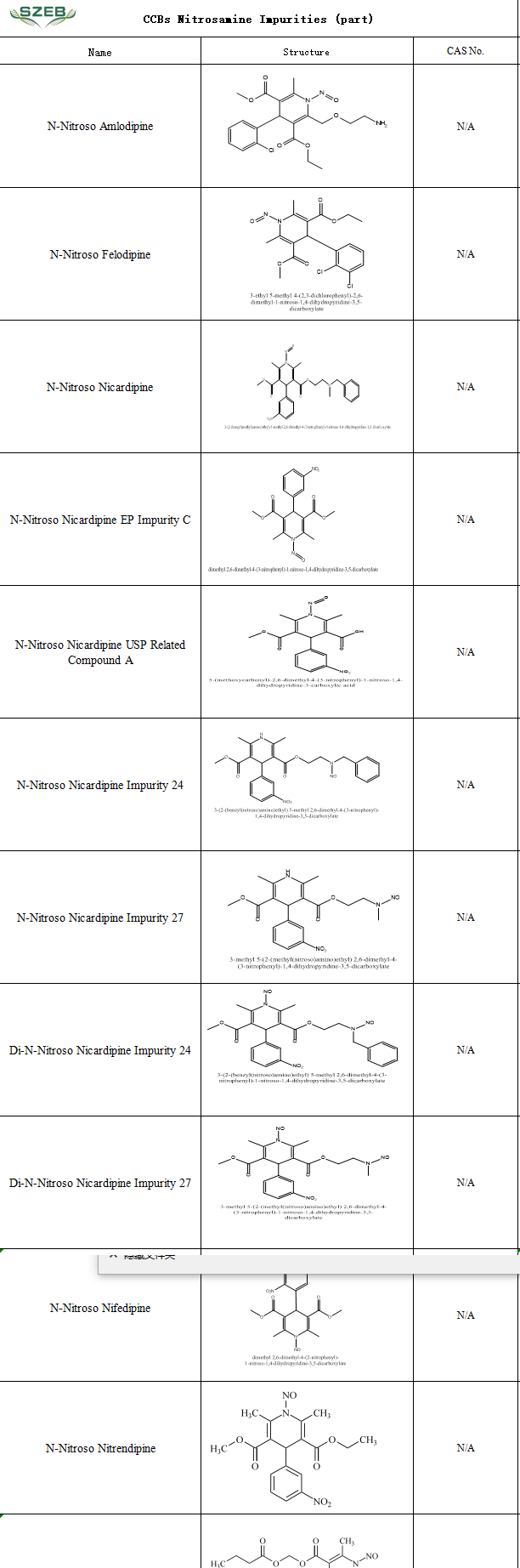
Nitrosamine impurity control remains a global regulatory priority. For CCBs—the most widely prescribed antihypertensive class—robust identification and quantification of these impurities are critical for drug quality assurance.
SZEB now offers a comprehensive portfolio of certified nitrosamine impurity references for CCBs, including amlodipine, nicardipine, nitrendipine, and nifedipine derivatives. These references enable precise impurity identification, method validation, and batch monitoring, ensuring patient safety by controlling potential genotoxic impurities .
Partial Catalog of Available References:
For detailed information, visit Website: www.ex-biotech.com , contact us by e-mail:sales@ex-biotech.com .






.jpg) Wechat
Wechat